Biology Terminology: The Complete Guide to Key Biological Terms
Biology is the study of life, but it comes with a language all its own — a set of terms and phrases that can overwhelm beginners and even advanced students. From the microscopic cells inside our bodies to the vast ecosystems of the planet, understanding biology terminology is essential to mastering the subject.
Why? Because terms are the tools scientists use to communicate complex ideas clearly and accurately. Using the correct terminology demonstrates expertise, authority, and trustworthiness (EEAT) in any scientific discussion, whether in school, research, or online content.
This guide will introduce you to the most important biology terms, explain them in easy-to-understand language, provide mnemonics and fun memory tips, and show you how to apply them confidently. Get information on Pantagonar
1. Top 50 Essential Biology Terms You Must Know
Let’s start by breaking down biology terminology into categories, so it’s easier to digest and remember.
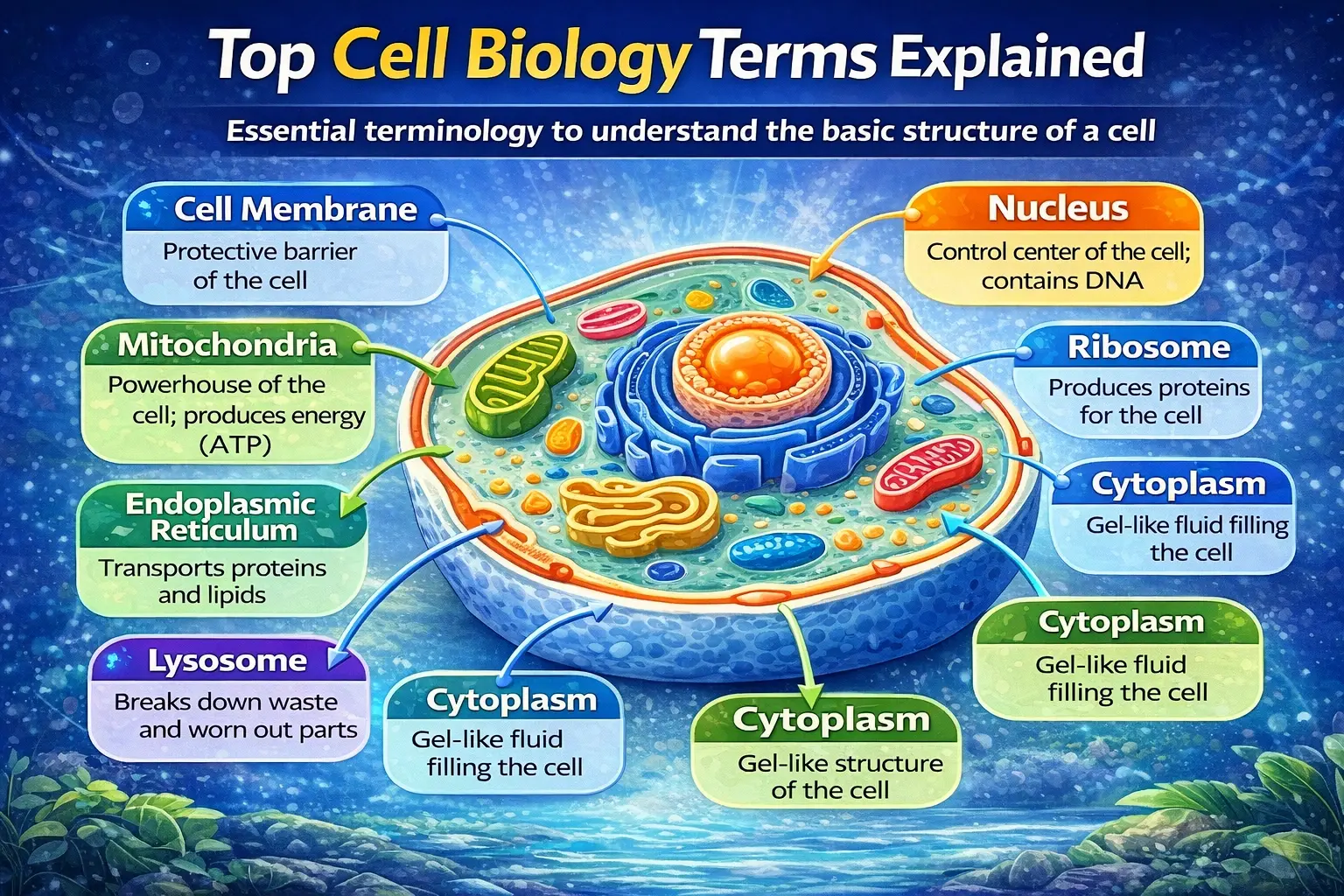
A. Cell Biology Terms
- Cell Membrane: A protective layer around the cell, like a security gate controlling what enters and exits.
- Nucleus: The control center of the cell, housing DNA and managing cell activities.
- Mitochondria: The “powerhouse” of the cell, generating energy through cellular respiration.
- Ribosome: Tiny structures producing proteins, often called the cell’s factories.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): A network for transporting proteins and lipids; think of it as the cell’s highway system.
- Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, packages, and ships proteins like a post office.
- Lysosome: The cell’s recycling center, breaking down waste and damaged organelles.
- Cytoplasm: Gel-like fluid filling the cell, supporting organelles.
- Chloroplast: Found in plant cells; converts sunlight into energy via photosynthesis.
- Centriole: Helps organize cell division.
B. Human Anatomy Terms
- Neuron: Nerve cells that transmit electrical signals throughout the body.
- Synapse: Junction between neurons where signals are transmitted.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange occurs.
- Ligament: Connective tissue that links bones together.
- Tendon: Connective tissue attaching muscles to bones.
- Dermis: Middle layer of skin containing nerves and blood vessels.
- Myocardium: Heart muscle responsible for pumping blood.
- Glomerulus: Tiny blood-filtering unit in the kidneys.
- Pancreas: Organ that produces insulin and digestive enzymes.
- Hypothalamus: Brain region controlling hormones, hunger, and temperature.
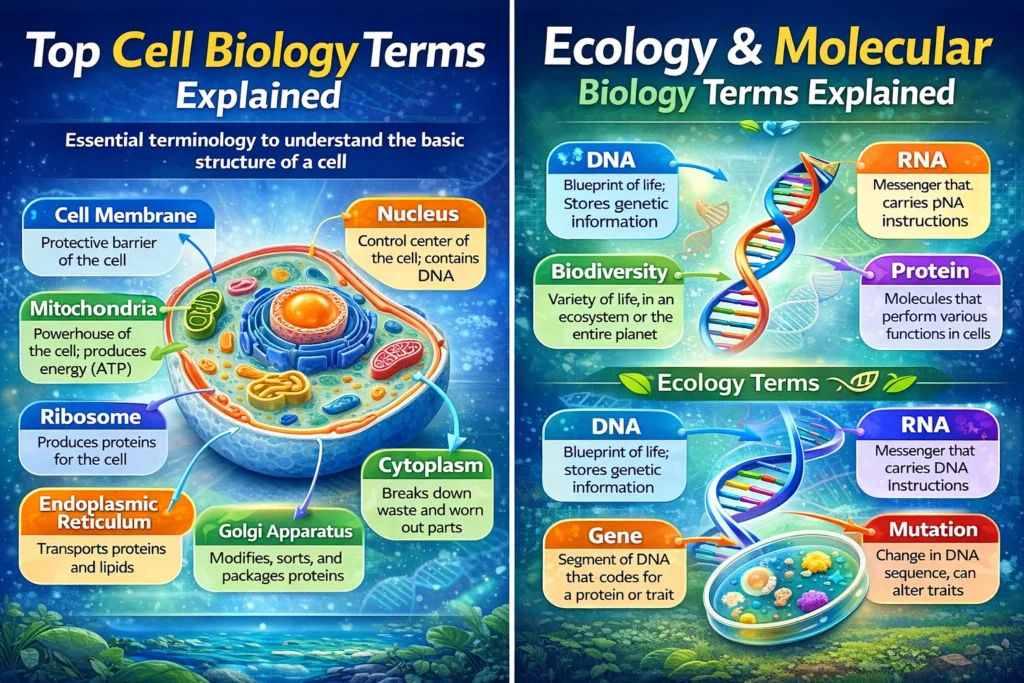
C. Molecular Biology Terms
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): Blueprint of life, carrying genetic instructions.
- RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): Messenger carrying DNA instructions for protein synthesis.
- Enzyme: Proteins that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions.
- Protein: Macromolecules performing structural, functional, and regulatory roles.
- Chromosome: DNA packaged into organized structures in the nucleus.
- Gene: Segment of DNA coding for a specific protein or trait.
- Mutation: Permanent change in DNA sequence that can affect traits.
- Allele: Different forms of the same gene.
- ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate): Energy currency of the cell.
- Replication: Process of copying DNA before cell division.
D. Ecology and Evolution Terms
- Ecosystem: Community of living organisms interacting with their environment.
- Biodiversity: Variety of life in an ecosystem or planet.
- Food Chain: Sequence of organisms showing who eats whom.
- Food Web: Complex network of interconnected food chains.
- Trophic Level: Position of an organism in a food chain.
- Habitat: Natural home of a species.
- Niche: Role of an organism in its ecosystem.
- Adaptation: Traits enabling an organism to survive in its environment.
- Speciation: Formation of new species through evolution.
- Natural Selection: Process where organisms better adapted to the environment survive and reproduce. Read more on about Article of overview of biology.
E. Genetics & Biotechnology Terms
- Genotype: Genetic makeup of an organism.
- Phenotype: Physical appearance or observable traits.
- Cloning: Producing genetically identical organisms.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): Technique to amplify DNA.
- Transcription: Copying DNA into RNA.
- Translation: Converting RNA into proteins.
- Recombinant DNA: DNA formed by combining genetic material from different sources.
- Genome: Complete set of an organism’s genes.
- Epigenetics: Study of changes in gene expression without altering DNA sequence.
- CRISPR: Gene-editing technology allowing precise modifications to DNA.
2. Fun Ways to Remember Biology Terminology
- Mnemonics: Use phrases like MRS GREN (Movement, Respiration, Sensitivity, Growth, Reproduction, Excretion, Nutrition) for life processes.
- Flashcards: Test yourself with visual cues for terms and definitions.
- Analogies: Compare mitochondria to power plants, ribosomes to factories, and neurons to electrical wires.
- Quizzes: Online tools like Quizlet or Kahoot make learning interactive and fun.
- Draw Diagrams: Visual representation improves memory retention for complex processes.
3. Common Mistakes Students Make
- Confusing osmosis vs diffusion.
- Misusing terms like gene vs allele.
- Overcomplicating explanations with unnecessary jargon.
- Forgetting context: e.g., DNA in molecular biology vs forensic science.
- Relying solely on memorization without practical application.
4. Expert Tips for Mastering Biology Vocabulary
- Read textbooks, research articles, and journals regularly.
- Join study groups for peer discussions.
- Use visual aids, including diagrams, info graphics, and videos.
- Review daily rather than cramming.
- Apply knowledge in practical experiments or observations.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How can I learn biology terminology fast?
A: Use mnemonics, flashcards, and relate terms to real-life examples.
Q2: Why is biology terminology important?
A: Accurate terminology ensures clarity, credibility, and better understanding of scientific concepts.
Q3: Are there online tools to memorize biology terms?
A: Yes, Quizlet, Khan Academy, and Biology Online provide interactive learning platforms.
Q4: How can I remember cell organelles easily?
A: Analogies work best: mitochondria = power plant, ribosome = protein factory.
Q5: Can biology terminology help in exams?
A: Absolutely! Using correct terms earns marks for clarity and scientific accuracy.